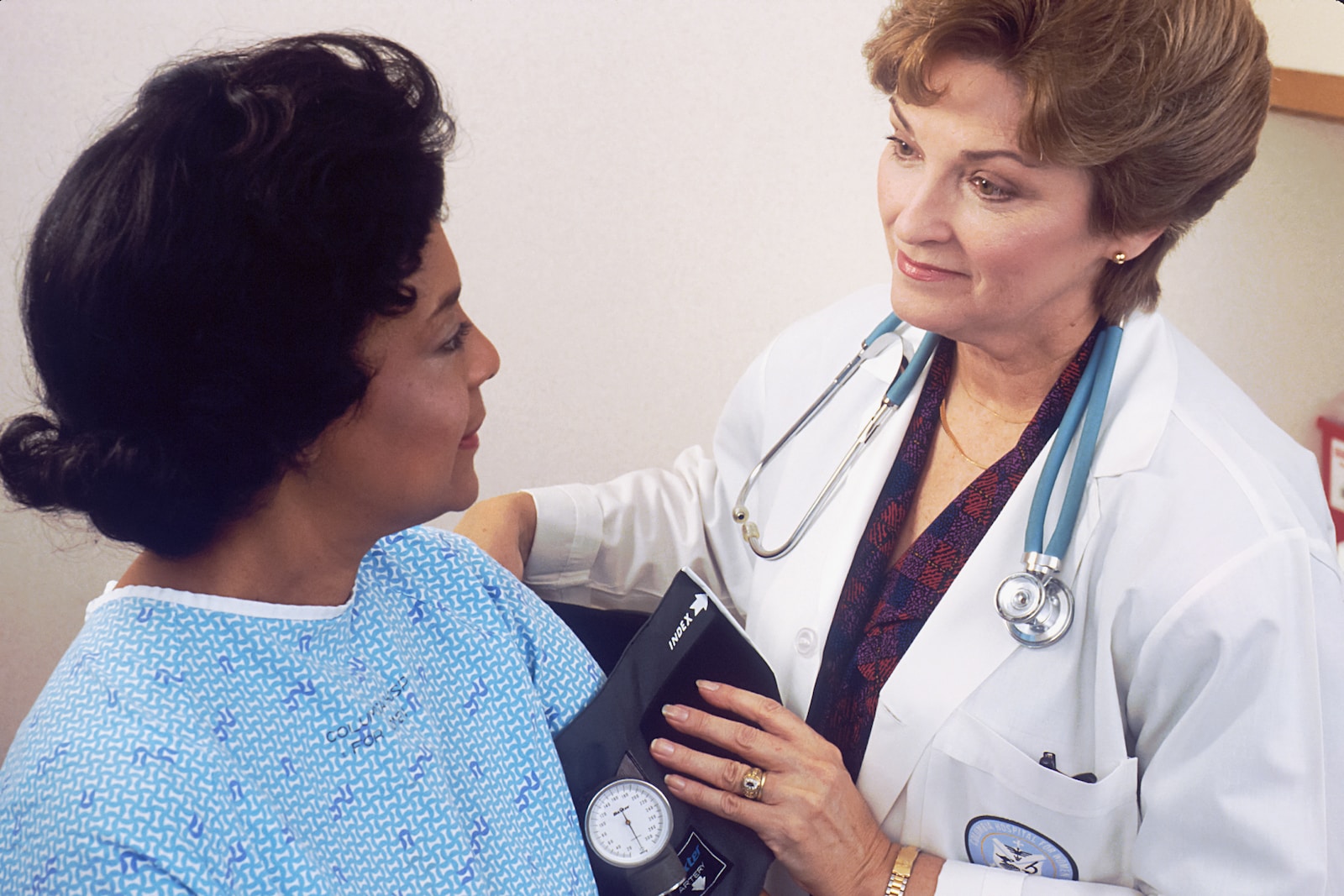
Women’s Normal Blood Pressure, the force exerted by blood against the walls of blood vessels, is a crucial indicator of cardiovascular health.
Women’s Normal Blood Pressure, the force exerted by blood against the walls of blood vessels, is a crucial indicator of cardiovascular health.
Maintaining normal blood pressure levels in women is essential for overall well-being and preventing various health complications.
This article’ll delve into what constitutes normal blood pressure for women, its significance, and ways to maintain optimal levels.
Understanding Blood Pressure Readings: Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and is expressed as two values:
- Systolic Blood Pressure: The higher number indicates the pressure in the arteries when the heart contracts and pumps blood into the circulation.
- Diastolic Blood Pressure: The lower number represents the pressure in the arteries when the heart is at rest between beats.
A normal blood pressure reading for adults is usually around 120/80 mmHg. However, blood pressure can vary based on factors such as age, activity level, and overall health.
The Significance of Normal Blood Pressure: Maintaining normal blood pressure is vital because high blood pressure (hypertension) can strain the heart and blood vessels, increasing the risk of serious health issues such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney problems. On the other hand, low blood pressure (hypotension) can lead to dizziness, fainting, and inadequate blood flow to vital organs.
Normal Blood Pressure in Women: While the normal blood pressure range is generally the same for both men and women, there are specific considerations for women based on age and life stages:
- Young Women: In women of reproductive age, hormonal fluctuations during the menstrual cycle can affect blood pressure. It is not uncommon for blood pressure levels to be slightly higher during the luteal phase (before menstruation) compared to the follicular phase.
- Pregnancy: Blood pressure may vary during pregnancy due to the body’s adaptations to support the growing fetus. Preeclampsia, a pregnancy-related condition characterized by high blood pressure and signs of organ damage, requires close monitoring and medical attention.
- Menopause: After menopause, women may experience changes in blood pressure due to hormonal shifts. Estrogen plays a role in regulating blood vessel health, and its decline during menopause can impact blood pressure.
Maintaining Normal Blood Pressure: To maintain normal blood pressure, women can adopt various lifestyle practices:
- A Balanced Diet: Emphasize a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy while reducing sodium, saturated fats, and added sugars.
- Regular Physical Activity: Engage in regular aerobic exercises like walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling, as well as strength training to support heart health.
- Manage Stress: Incorporate stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, or hobbies to promote relaxation.
- Limit Alcohol and Tobacco: Moderation in alcohol consumption and avoiding smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke can contribute to better blood pressure control.
- Regular Check-ups: Regularly monitor blood pressure and attend routine medical check-ups to detect and address any potential issues early on.
Conclusion:
Normal blood pressure is a vital sign of a woman’s overall health. It is crucial for women to understand their blood pressure readings, monitor them regularly, and make lifestyle choices that support optimal cardiovascular health. By adopting a balanced diet, staying physically active, managing stress, and avoiding harmful habits, women can empower themselves to maintain normal blood pressure levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases in the long run. Regular consultation with healthcare professionals is essential to ensure comprehensive health management and early intervention if necessary.